fungi life cycle pdf
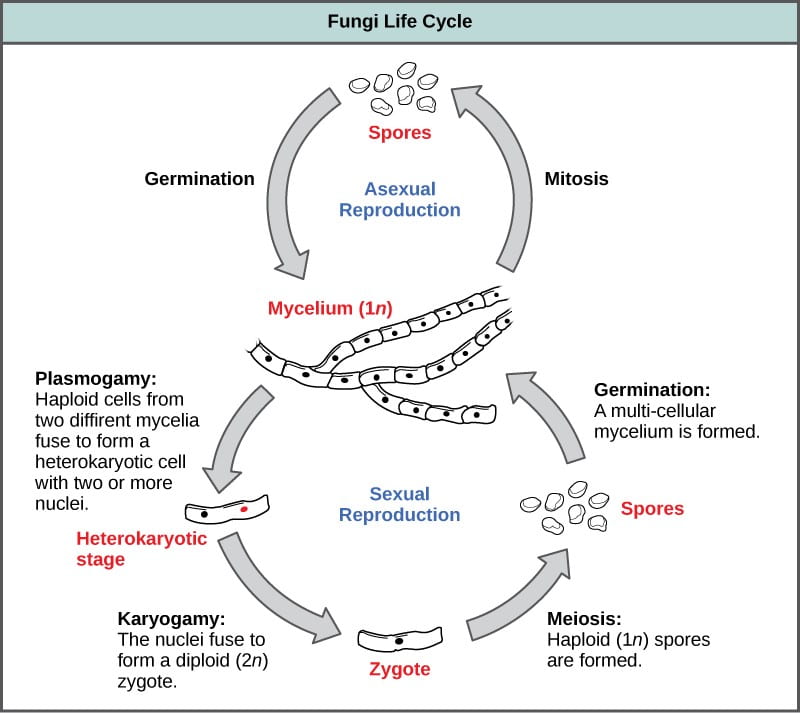
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins with the formation of the zygote the diploid cell resulting from fusion of two haploid sex cells. On-screen Show Other titles.

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Important Features Non-mycelial Ascomycetes do not produce fruiting bodies or ascocarps.

. - Asexual - Sporangia produces haploid spores. Reproduction in fungi A. One of these migrates into the germ tube.
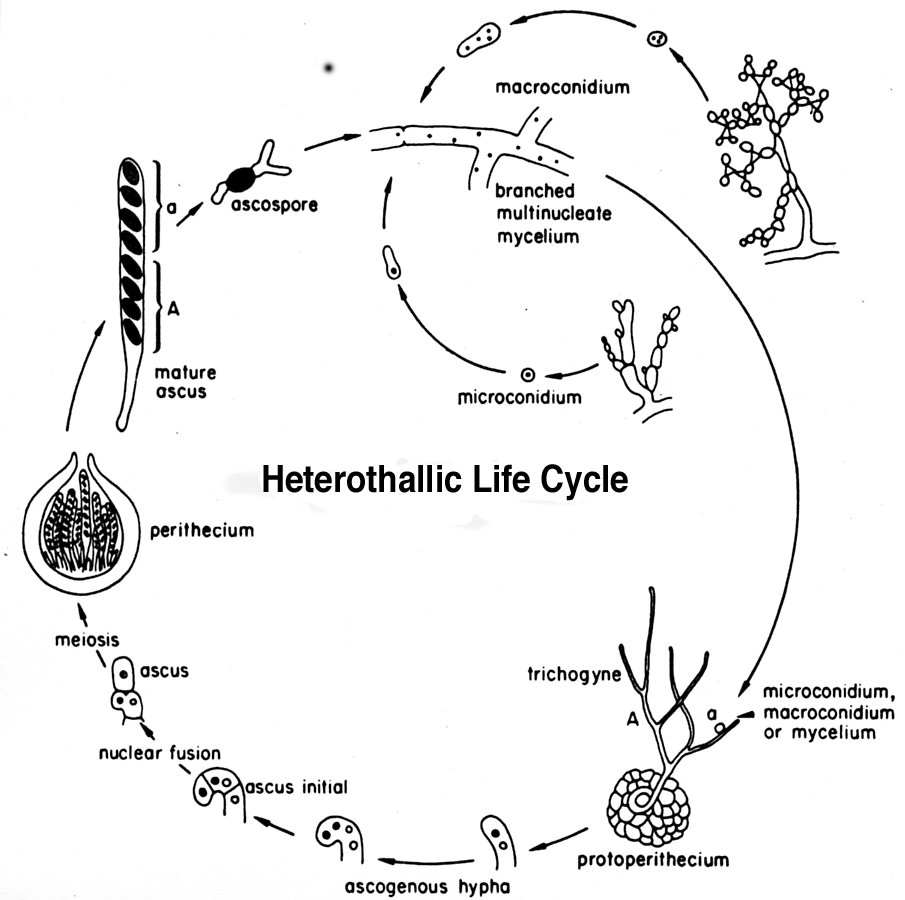
Life cycle of fungi. It consists of the ascospores parent mycelium antheridia when present and young ascogonia. The life cycle of rusts can be complex.
Reproduce by budding fission or both. Bernice Speer Last modified by. Mycorrhiza is a term to indicate i fungus association with stem ii bacteria association with root iii fungi association with root iv study of fungi 92.
Bernice Speer Created Date. These are called sporangiophores. 9272008 83607 PM Document presentation format.
Ascospores are produced in a naked ascus. All about spores and how they work in your garden ecosystem to help. Reproduction is by budding of yeast cells.
All fungi begin their life cycle in. Formed on or in specialized structures. Enroll Today Dive Deep into the World of Biology.
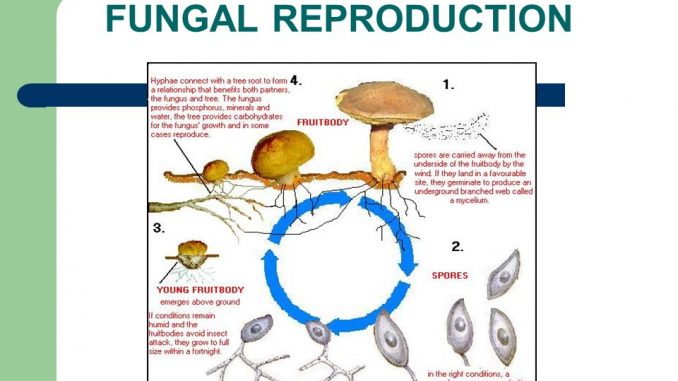
How fungi establish themselves and how you can help make this happen in your garden. Kulat breeding cycle. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium.
It is done by the formation of conidia. Paul Minnesota USA Maria E Ordonez Quito Ecuador James V Groth Coleville Washington USA The rust fungi are a monophyletic group of approximately 7000 species in the basidiomycota and are highly specialized obligate parasites of plants. Are chemoheterotrophs require organic compounds for both carbon and energy sources and fungi lack chlorophyll and are therefore not autotrophic.
Terrestrial orchids produce protocorms that may remain belowground for several years before they emerge and produce their first leaves. The single nucleus of the resting spore divides early in germination. While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually.
Fungi early in their lives. Economic importance of fungi Beneficial fungi Fungi can be used as a source of food eg. Tropical orchids produce protocorms that quickly turn green and develop leaves.
Which letters are haploid diploid and nursing. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way. Mushroom Yeasts can be used to make bread and alcohols such as wine and beer anaerobic respiration C 6H 12O 6 2C 2H 5OH 2CO 2 Ethanol Baker Brewer Note.
The Rust Fungi James A Kolmer USDA-ARS St. Kulat breeding cycle. Biology of Fungi Lecture 2.
Plasmodiophora brassicae l Infection of plant roots leads to club foot l Plant responds to infection by P. Kulat breeding cycle. Not all fungi reproduce in the same way.
Meiosis reduction division restores the haploid number of chromosomes and initiates the. There are accessory means of multiplication of this phase in the life cycle. Occurrence Habitat Ubiquitousfoundeverywhereonsugary substratum.
The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Brundrett 1990 showed the same cycle pattern using an alternative. Nucleus and Cell walls composed of chitin.
By hitching a ride on another organism or even the wind these spores can travel great. Life Cycle of Fungi. With the host protoplasm.
Kulat breeding cycle. Candida albicans ascomycete is an asexual animal pathogen. Their tips swell to produce a sporangium.
Sexual Reproduction of Fungi Spore Haploid. While some fungi reproduce sexually others reproduce asexually. Protocorms Orchid seeds germinate into protocorms that occur in a variety of shapes.
In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase. This is similar to sperm and eggs which are similar to human sex cells. Diversity of Fungi Page 4 of 16 u Phylum Plasmodiophoromycota Q Obligate intracellular parasites of plants algae or fungi Q Best example.
They obtain their nutrients by absorption. Spore germ hypha mature mycelium. Monokaryotic mycelium uninucleate Mycelium contains single nucleus that usually forms part of haplophase in the life cycle of fungi.
In the life cycle it starts with the formation of ascospores and ends with the formation of dikaryons in the ascogonium. Most of the molds indoors are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. Spore Haploid The spore phase is the initial stage of the fungal life cycle.
All fungi possess cell wall made of chitin. Formation of Zygospore ascospores or basidiospores. Ad Comprehensive Biology Course.
Life Cycle of Fungi. The life cycle of fungi can follow many different patterns. The whole life cycle of wood-loving macro-fungi from mushroom back around to mushroom.
Brassicae by undergoing rapid cell expansion and division forming galls that require. Dikaryotization is an essential feature in the life-cycle of rusts smuts and some allied fungi Petersen 1974 Littlefield Heath 1979 Coelho et al. Life cycle of Rhizopus.
When two host species are required for completion of parasitic fungi life-cycle this condition is described as i autoecism ii autotrophic iii heteroecism iv heterokaryotic 91. Cycles in fungi beginning with relatively simple life cycles Please realize that each of the major groups of fungi has a diversity of life cycles beyond those listed here. Filamentous fungi possess a yeast-like phase at some point in their life cycle.
Intercellular hyphae of many fungi especially of obligate parasites of plants fungi causing downy mildews powdery mildews and rusts obtain nutrients through haustoria. With the elongation of the germ tube most of the mitochondria migrate into it and become concentrated near the tip. All fungi start as haploid spores which means they only have one copy of their genetic information.
The life cycle of fungi has many different patterns based on the species of the fungi. Evolution Characteristics and Life Cycle Author. Therefore we are going to look at the life cycle of a fungi in asexual and sexual stage.
A dikaryotic filament developed from. For most of the molds indoors fungi are considered to go through a four-stage life cycle. How fungi are different from plants and actually are a lot more like animals this includes you.
Kulat breeding cycle. - Asexual - Sporangia produces haploid spores. - Asexual - Sporangia produces haploid spores.
Copy link Link copied. The electron-dense wall layer W 2 remains at the base of the germ tube and around the spore. The CO 2 produced by yeast causes the dough to rise - the heat evaporates the ethanol.

Life Cycle Of Penicillium Sp Download Scientific Diagram
Reproduction In Fungi Asexual And Sexual Methods Online Biology Notes
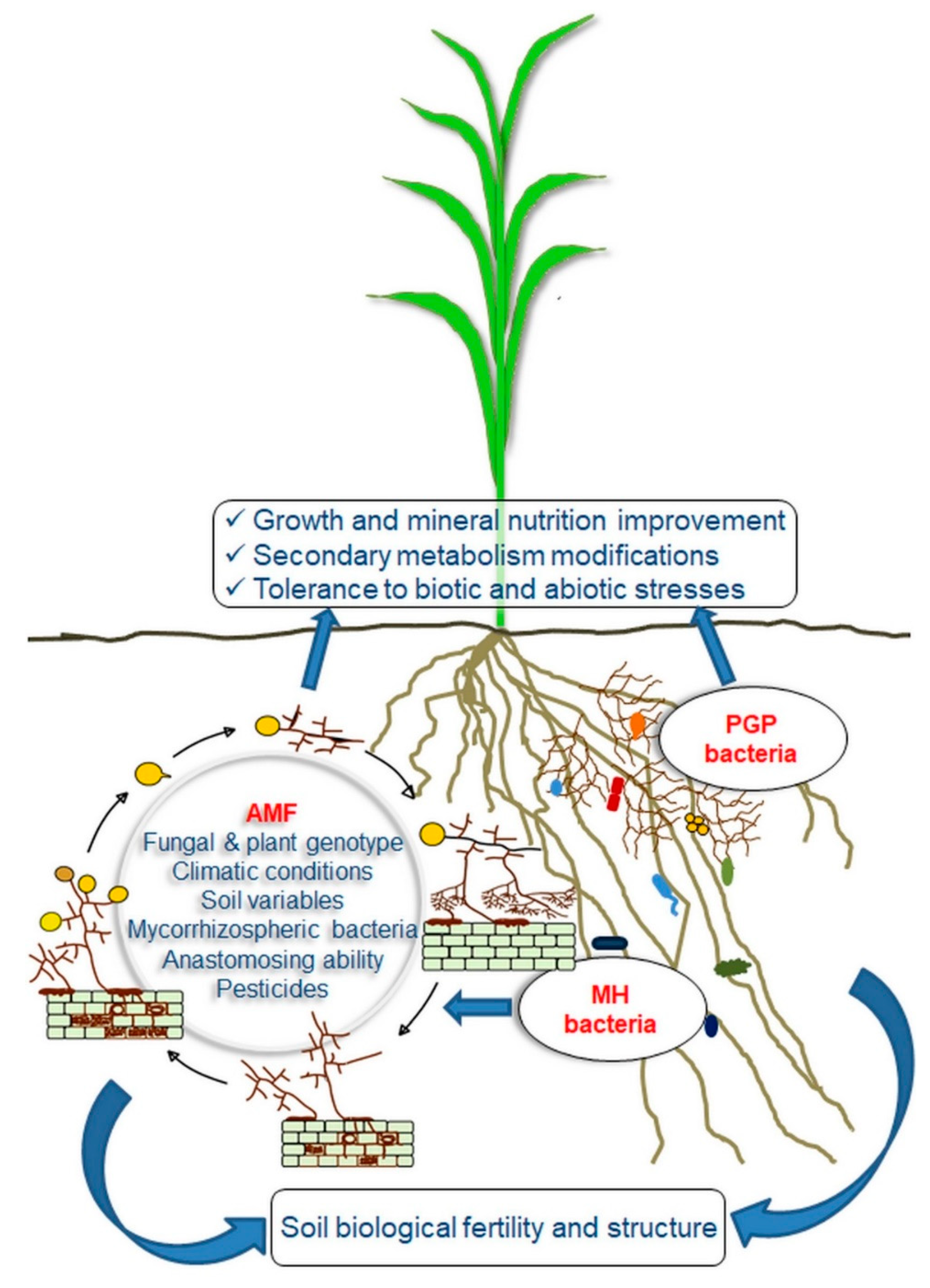
Agronomy Free Full Text Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi And Associated Microbiota As Plant Biostimulants Research Strategies For The Selection Of The Best Performing Inocula Html

Aquatic Fungi An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Life Cycle Of The Ascomycota Download Scientific Diagram

Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Conducting The Hyphosphere Bacterial Orchestra Trends In Plant Science

Basidiomycota Life Cycle Study Com

Life Cycle Of A Macrocyclic Heteroecious Rust A Mature Diploid Download Scientific Diagram

3 Life Cycle Of A Heteroecious Macrocyclic Rust Fungus Melampsora Download Scientific Diagram

Mushroom Life Cycle Kidspressmagazine Com Stuffed Mushrooms Science For Kids Life Cycles
Classification Of Fungi Biology Ii
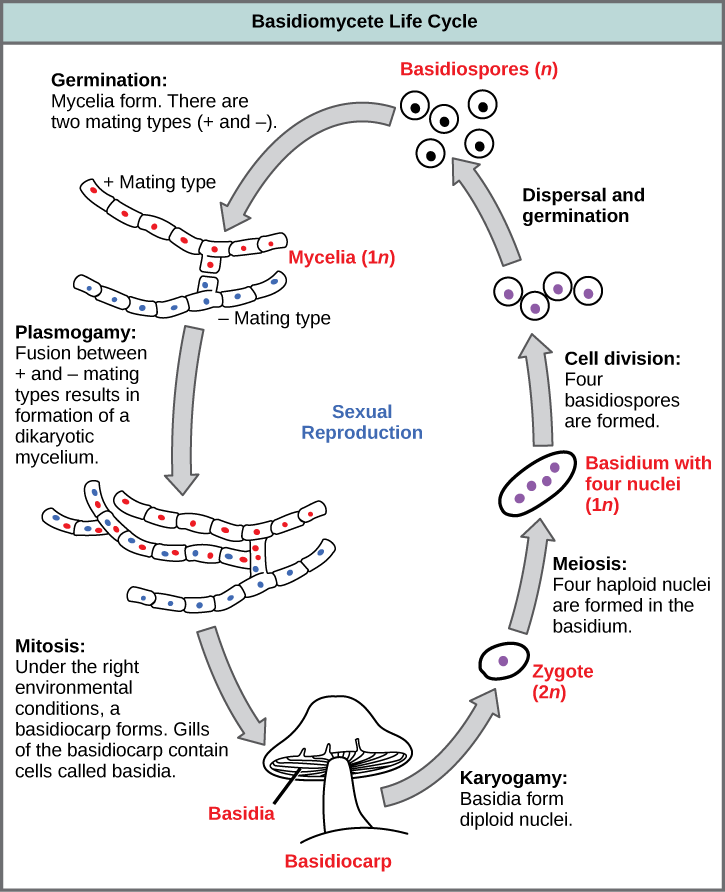
Basidiomycota The Club Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii
Fungi General Characteristics Classification Morphology Pathogenecity
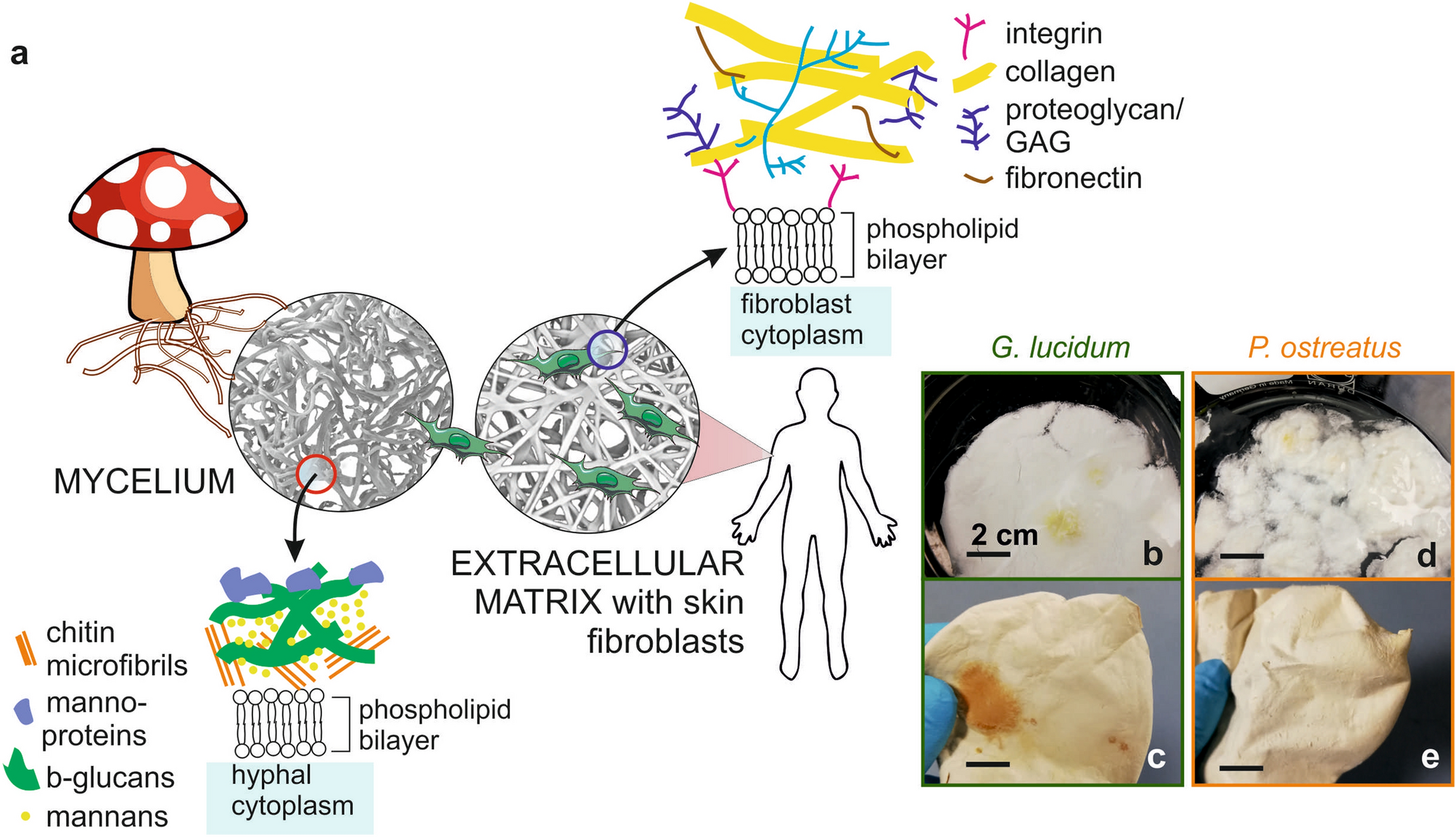
Advanced Mycelium Materials As Potential Self Growing Biomedical Scaffolds Scientific Reports